Guidelines for Lead in Drinking Water in the Fraser Valley
Lead FAQ for the Fraser Valley
Lead (Pb) is a naturally occurring toxic metal found in water, soil, and air. Lead is a neurotoxin, a carcinogen, and a heavy metal that bioaccumulates in the body Lead enters drinking water primarily through the corrosion of plumbing material. Exposure to lead may cause health issues ranging from stomach disorders to possible brain damage.
If there is any concern about lead in your drinking water it’s vital to test your water for lead contamination.
How can lead get into your drinking water?
Lead occurs naturally within bedrock ore, but lead is seldom detected in source water.
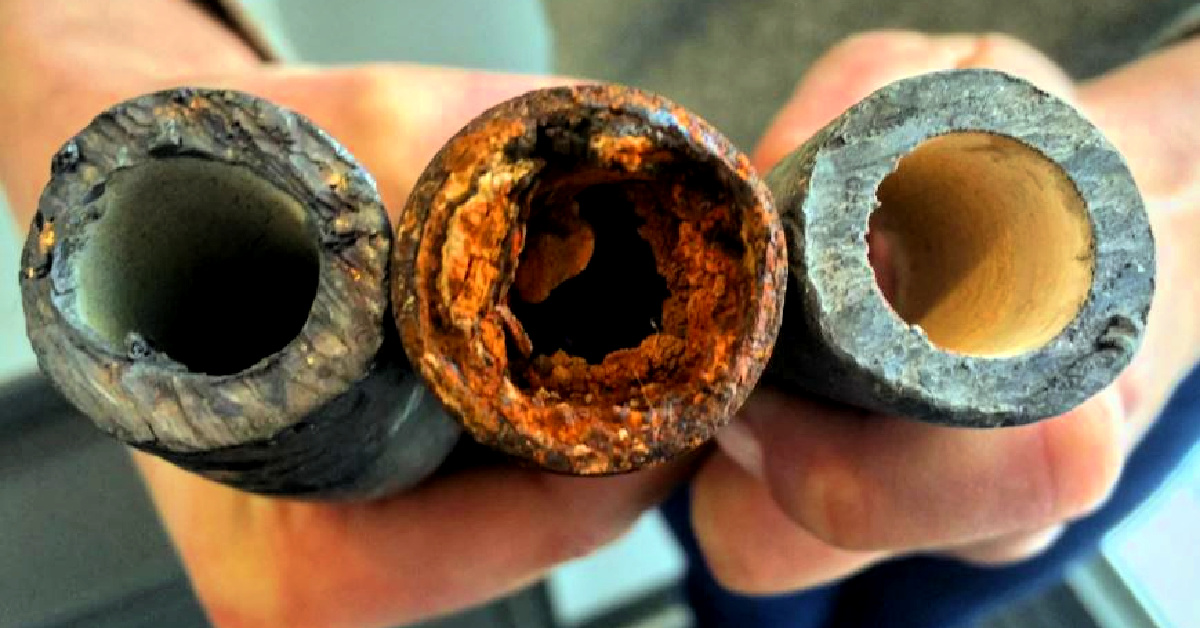
The main source of lead is leached into drinking water from plumbing such as water mains, pipes, solder, water faucets, pipe fittings, and older galvanized water well liners and possibly old well pumps systems in the Fraser Valley with pumps suspended on galvanized steel pipe with fittings and pit-less adapters that are not lead-free.
Is it safe to drink water from lead pipes?
The amount of lead that will dissolve into drinking water will depend on the water chemistry including pH, alkalinity, water temperature, water hardness, length of water pipe, and contact time of water and contaminated plumbing material.
Corrosive water in the industry is also known as “aggressive water.” Aggressive water is water that will dissolve materials that it comes into contact with.
Corrosion of lead from plumbing systems is more of a concern to the homeowner since it is a significant health hazard even in the smallest of amount. Lead contaminated water will leave no visual indication and has no obvious taste or odor in drinking water.
If replacing lead plumbing or fittings on a pressure system here is a full comprehensive tutorial for pressure tanks and adjusting pressure switch on well pump system.
Health Effects of Lead in Drinking Water
Lead in Drinking Water Health Canada
Two different categories:
Lead in Drinking Water in the Fraser Valley – Canadian Maximum Acceptable Concentrations (MAC) 0.005 mg/L are based upon potential adverse health effects but, water test results that exceed 0.005 mg/L do not necessarily indicate any immediate health problem. This is because whenever possible MACs are developed to be low enough that years of exposure at this level would still only increase the health risk slightly.
However, corrective actions should be taken if water test results exceed the MAC in order to remove any potential for increased health risk.
Aesthetic Objectives (AO) are not based upon health effects, but water test results that exceed these levels may indicate that the drinking water could have objectionable taste, odour, appearance or other factors including microbiological concerns such as viruses, bacteria and protozoa.
Corrective actions are recommended if water test results exceed the AO but may not be necessary.

Fraser Valley Drinking Water - Lead
How Much Lead in Drinking Water is Toxic?
Maximum Acceptable Concentration for Drinking Water in Canada = 0.005 mg/L according to the new reporting limit for lead for the Canadian Drinking Water Quality Guidelines update as of April 2019.
Lead in drinking water has no taste, smell, or color. It can only be detected through a chemical water test for lead.
The Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality set a maximum acceptable concentration of 0.005 mg/L (5 parts per billion) for total lead in drinking water, measured at the tap. Every effort should be made to maintain lead levels in drinking water and keeping it as low as possible
Lead in drinking water can cause a variety of adverse health effects. Children, infants, and unborn children are more strongly affected by exposure to lead because their bodies absorb lead more readily than adults.
A child’s brain and nervous system is known to be more sensitive to the effects of lead than older children and adults.
Children Exposed to Lead
Children exposed to lead above .005 mg/L may include:
- Damage to the brain and nervous system
- Delays in physical and mental development
- Behaviour and learning disabilities
- Hearing disorders
Exposure to lead can affect the brain development of babies and younger children. Lead exposure can cause other health problems with heart, kidney, and reproductive health in babies, children and adults.
Young children (under than 6 years in age) will have the highest risk for health effects because they’re still developing. Younger children also absorb lead easier and quicker than adults.
Babies whose formula or juice is prepared with tap water are at risk of being exposed to lead because the water used makes up 40 to 60% of a baby’s intake. The water that older children and adults drink only makes up 10 to 20% of their intake because they ingest far more solids
Pregnant women can even pass lead to their unborn children. Lead can be present in breast milk, it’s vital for breastfeeding women to lower lead exposure as much as possible.
If you’re pregnant or have children younger than 6 years-old, see your doctor if your drinking water exceeds limits or you have an concern about lead exposure
Possible adult health effects when exposed to lead:
- Increased blood pressure
- Anemia
- Nerve disorders
- Muscle & joint pain
- Irritability
- Kidney damage
- Digestive problems
- Memory loss
- Fatigue
- Headaches
Exposure to lead can affect the brain development of babies and younger children. Lead exposure can cause other health problems with heart, kidney, and reproductive health in babies, children and adults.
Young children (under than 6 years in age) will have the highest risk for health effects because they’re still developing. Younger children also absorb lead easier and quicker than adults.
Babies whose formula or juice is prepared with tap water are at risk of being exposed to lead because the water used makes up 40 to 60% of a baby’s intake. The water that older children and adults drink only makes up 10 to 20% of their intake because they ingest far more solids
Pregnant women can even pass lead to their unborn children. Lead can be present in breast milk, it’s vital for breastfeeding women to lower lead exposure as much as possible.
If you’re pregnant or have children younger than 6 years-old, see your doctor if your drinking water exceeds limits or you have an concern about lead exposure
The lead risk to human health is only through the ingestion of lead such as drinking, cooking, brushing of teeth, etc. Lead levels in well water > 0.005 mg/L is fine for showers, baths, handwashing, dishwashing, and general cleaning uses.
How to test for lead in water in the Fraser Valley?
Regularly water testing for the standard chemical parameters, including lead. The Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality sets out parameters of substances that may be found in drinking water.
The lead risk to human health is only through the ingestion of lead such as drinking, cooking, brushing of teeth, etc. Lead levels in well water > 0.005 mg/L is fine for showers, baths, handwashing, dishwashing, and general cleaning uses.
Testing your water for lead in the Fraser Valley is easy!
Fortunately regular water testing in the Fraser Valley is easy! Typically a Fraser Valley water test kit that tests for standard chemical parameters will include lead. If you rather test your drinking water just for lead a lead water test kit is perfect! The Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality sets out parameters of substances that may be found in drinking water.
How to Test for Lead in Water
Water filters for lead in drinking water
All well water testing, lead water test, water quality testing, and water test kits should be issued and conducted by an accredited water testing laboratory. Local accredited water testing laboratories serving the Fraser Valley will have a lead water test kit.
Well water testing for lead
If your water is drawn from a water well take a second lead test. This time take a raw water sample from the water well before it enters your home or building. Hopefully this will help determine if the lead is actually present in the groundwater or if the plumbing pipe or fittings is responsible for the lead contamination issue.
Should I test my city water for lead?
If on a city water supply one water sample should be collected prior to flushing the water (running the tap for at least two minutes) and another separate water sample collected after flushing the water line.
When should a lead water sample be taken?
Taking the first sample in the morning after the water has been in contact with the water pipe for an extended period may be ideal then the second sample as described.
For water sampling use the special water sampling bottles provided in the water test kit. Follow water testing instructions for proper water sampling procedures, not following proper water testing procedure may cause the water analysis report to be false or fail for some water parameters.
How to purchase a lead water test kit in the Fraser Valley?
For more information on local water testing for lead in drinking water in the Fraser Valley, please visit Tap Score. Water testing costs will vary depending on the scope and the number of parameters being tested.
What is the best way to remove lead from drinking water?
Once you have submitted your water sample and are waiting for your water test report, you may want to use a safe alternate source of water for drinking, food washing, cooking, and dental until a further decision is made.
If excessive lead is found to be greater than 0.005 mg/L in your first lead water test, it’s important to determine the source of the lead.
If the source of lead is corrosion of lead-containing plumbing materials, consider the following options:
1 – Remove the source of lead
2 – Flush faucets until the water runs as cold as possible before using the water for drinking, cooking, or teeth brushing.
3 – Avoid using hot tap water for drinking, cooking, or making baby formula.
4 – Adjust pH so water is less corrosive (for more information, see our fact sheets on pH and corrosive water).
5 – Use a properly designed water treatment system to reduce lead in your drinking water
6 – Use an alternative water source, such as bottled water or another well that has been tested and found to be safe.
Can lead be removed with a lead water filter?
Lead cannot be removed from water through boiling. In fact, the boiling water may even increase the concentration of lead.
If the groundwater source is found to be contaminated with lead prior to entering the home, flushing the faucet will not be effective. Consider the following water treatment systems to effectively reduce lead levels:
• Cation exchange
• Distillation
• Reverse osmosis
• Lead water treatment system with certification NSF Standard No. 53 for reduction of lead in drinking water
Purchase a water treatment system or water filtration system that has been certified to meet the current NSF standards (National Sanitation Foundation) for lead reduction in drinking water.
NSF International is an accredited, independent third-party certification body that tests and certifies products to verify they meet these public health and safety standards. Home water treatment systems and that meet these standards bear the NSF mark. NSF International is a non-profit, non-governmental organization that sets health and safety standards for manufacturers in 80 countries around the world.
Once a water treatment system or water filtration system has been installed, re-test your water to ensure the water treatment system is working properly.
It’s crucial to maintain the water treatment system according to the instructions of your local water treatment expert to ensure safe and long-term supply of drinking water.
For more information on the best water treatment system for lead contaminated water contact your local water treatment experts.
Considerations for water softener for lead removal
If the pH of lead contaminated water is below 7, cation exchange will typically remove lead.
If the pH of the lead contaminated water is above 7, the dissolved lead might be in a form that cannot be easily removed using by using a water softener or cation exchange. This may affect the efficiency of your water treatment system.